What Everybody Ought To Know About Operating Cash Flow Interest Expense How To Find The Retained Earnings On A Balance Sheet
Cash in from sales, cash out for operating expenses, etc.
Operating cash flow interest expense. Interest expense reduces a company’s profitability by increasing its operating costs. Income from operations of $652 million; An interest expense refers to the cost incurred by companies for debt finance.
76% reimbursable prospect pipeline 15x ending backlog with opportunities across all three segments revamped capital structure lowers interest expense while supporting future growth anticipate improved cash flow. One such item that affects two areas within the cash flow statement includes interest. Interest coverage ratio (icr) = ebit ÷.
87% reimbursable increased backlog by over 10% each of the past two years to $29.4 billion; Operating cash flow indicates whether a company can generate sufficient. Record adjusted ebitda margin fourth.
Profitability and cash flow analysis: Usually, interest expense is a part of the income statement for all companies. Ias 7 statement of cash flows requires an entity to present a statement of cash flows as an integral part of its primary financial statements.
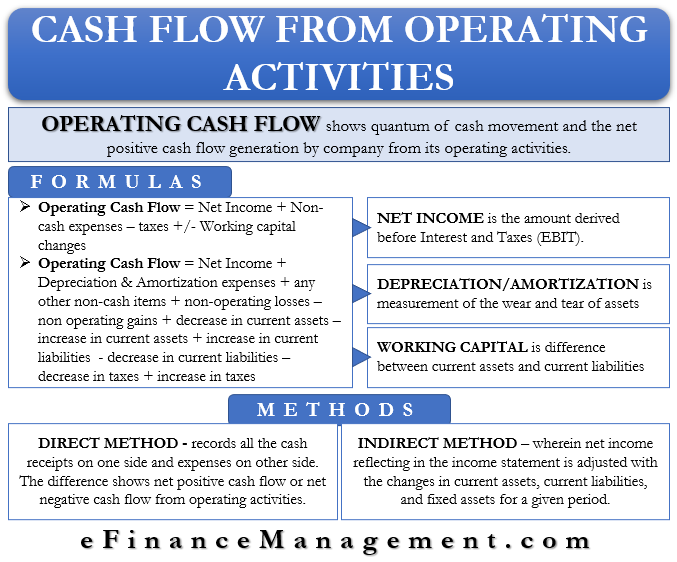
It’s calculated as revenue minus operating expenses. The operating cash flow ratio is a measure of how readily current liabilities are covered by the cash flows generated from. Is interest expense an operating expense?
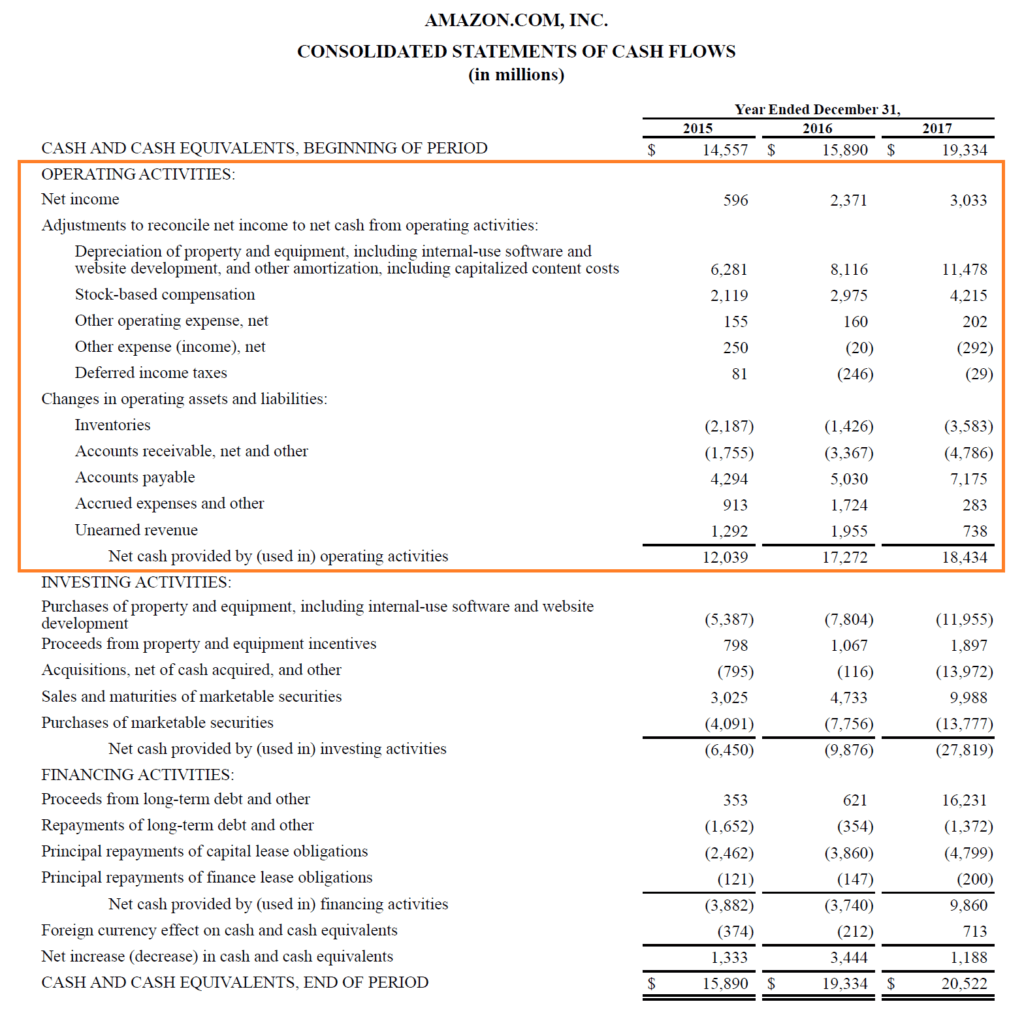
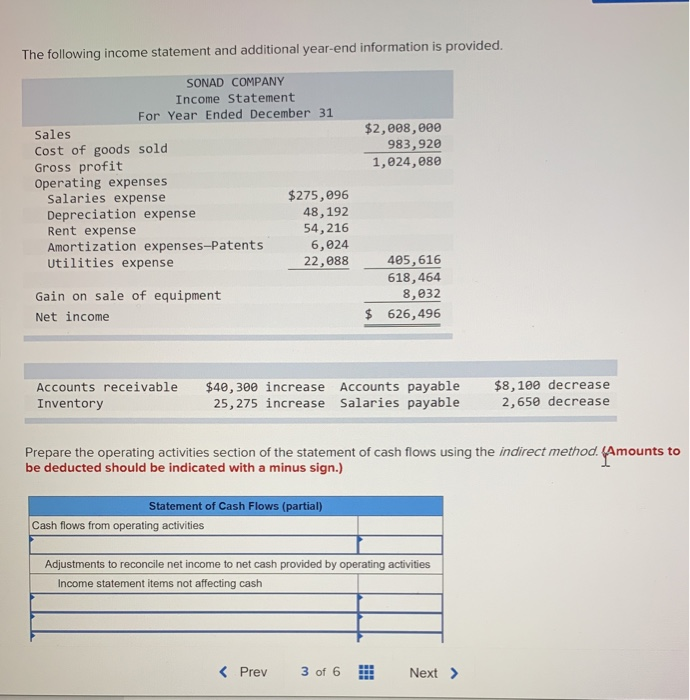
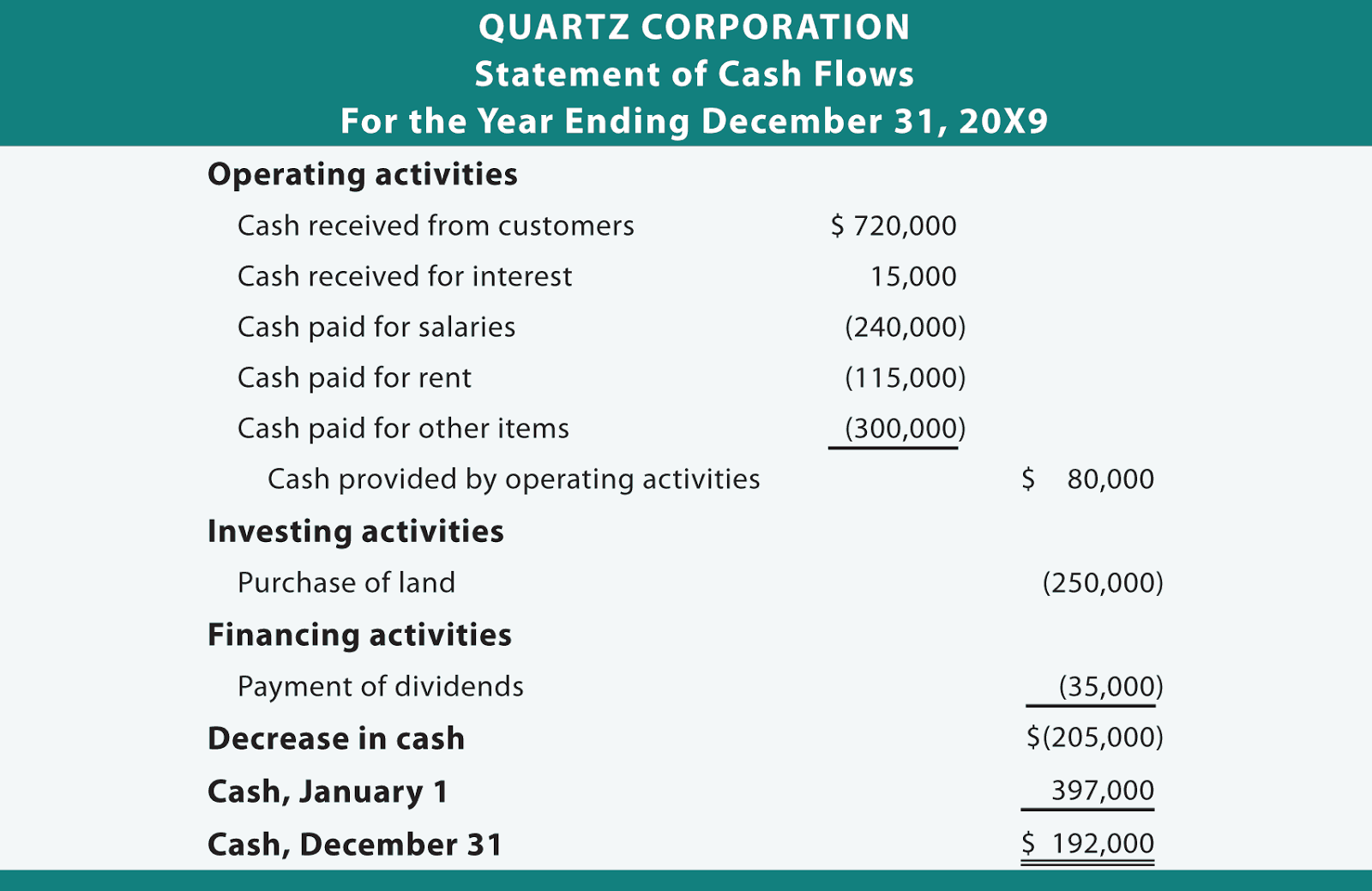
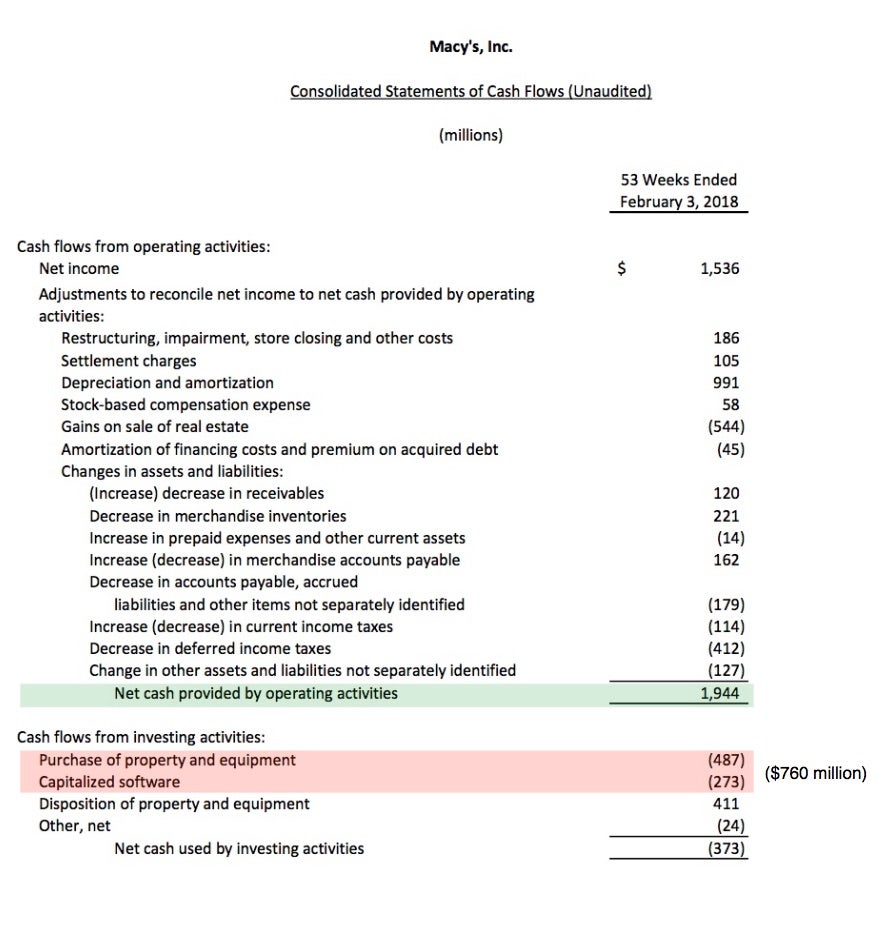
Taxes paid are generally classified as operating cash flows. Operating cash flow (or sometimes called “cash from operations”) is a measure of cash generated (or consumed) by a business from its normal operating activities. Partial statement of cash flow:
The income statement is reported per accounting standards established by u.s. If the indirect method is used, amounts of taxes paid during the period must be disclosed. As such, it can be misleading to include interest expense when trying to assess a company’s ability to generate cash.
Cash flow from operating activities (cfo) indicates the amount of money a company brings in from its ongoing, regular business activities, such as manufacturing and selling goods or providing a. Gaap, which has its shortcomings in reflecting the actual liquidity (i.e. Operating cash flow (ocf) is a measure of the amount of cash generated by a company's normal business operations.
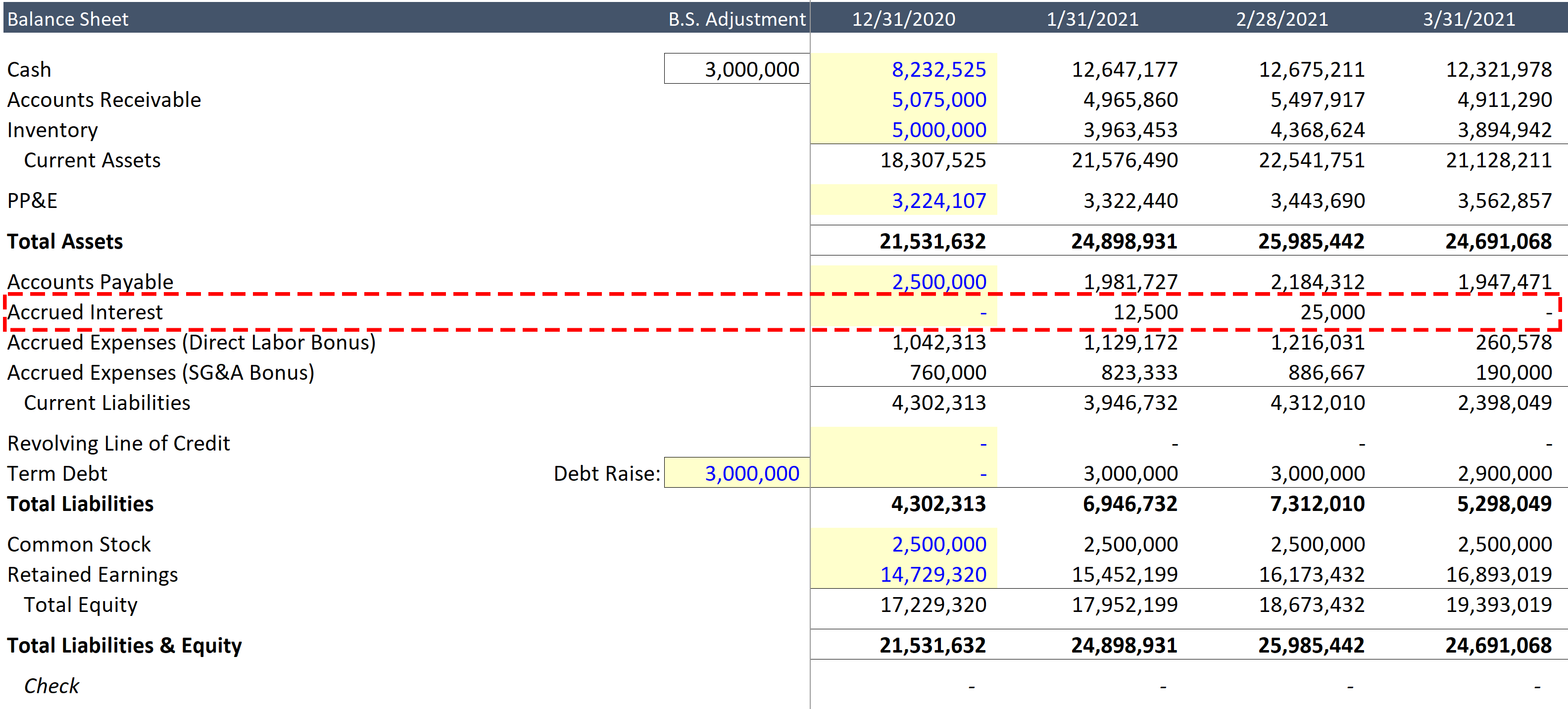
Where does interest expense go on the financial statements? Taxes paid should be classified within operating cash flows unless specific identification with a financing or investing activity exists. Even though interest expense lowers your cash flow and is recorded in the operating activities section of your company’s cash flow statement and in the nonoperating expenses of its.
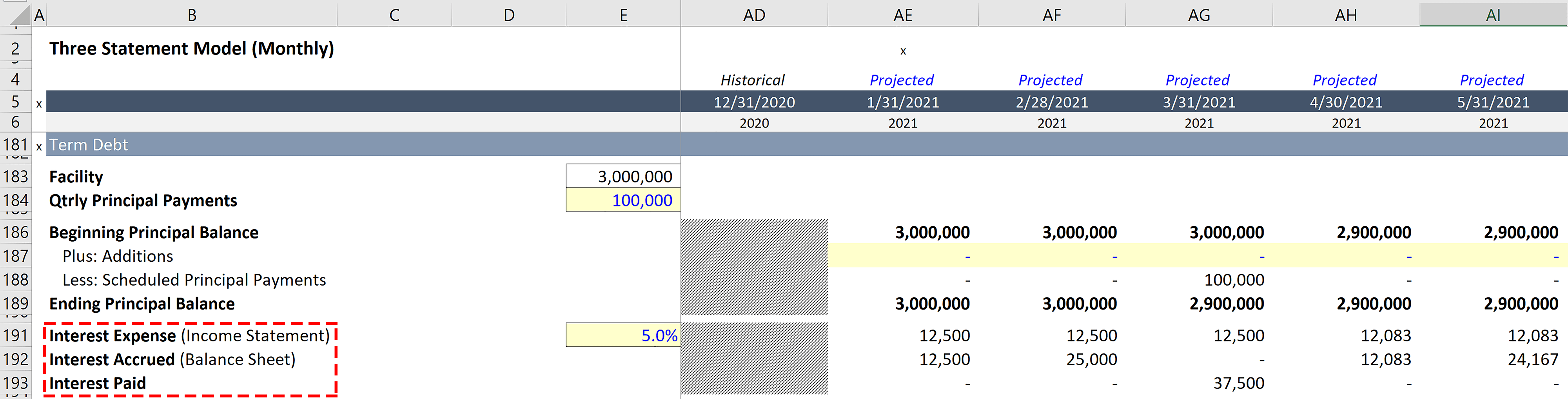
Interest expense = average balance of debt obligation x interest rate. When analyzing the cash flow statement, it is important to consider the impact of interest expense on the company’s net income and cash flow from operating activities. Repayment on loan (50,000) cash flow from issuing bonds:

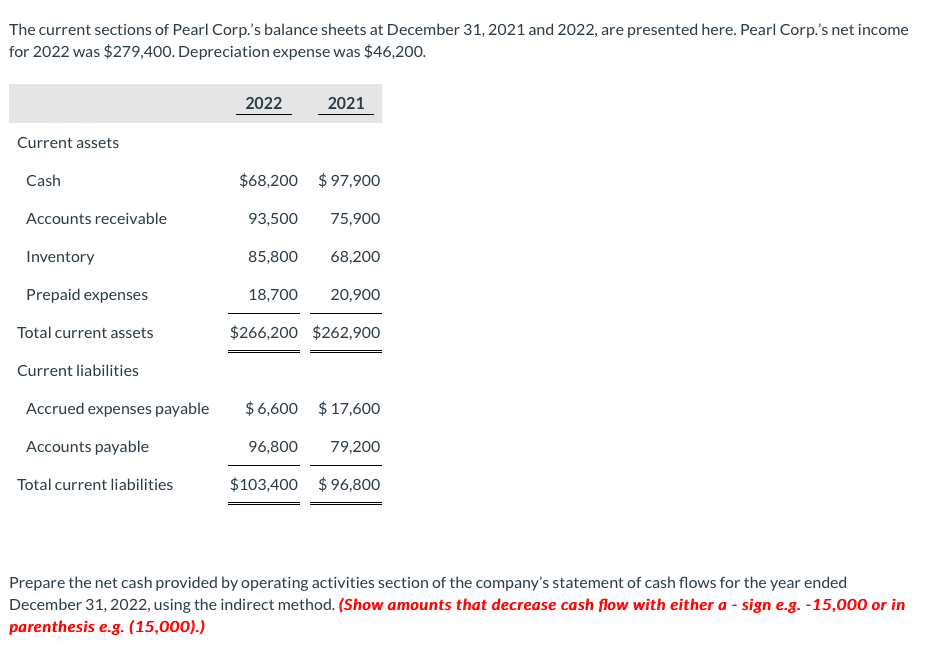
![Exercices chap 2 with solutions combined[ 5141] 5. Calculating OCF](https://d20ohkaloyme4g.cloudfront.net/img/document_thumbnails/1d6fbfe40c4ad7e6e8b4ea5adbe972f6/thumb_1200_1553.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Understanding_the_Cash_Flow_Statement_Jul_2020-01-013298d8e8ac425cb2ccd753e04bf8b6.jpg)