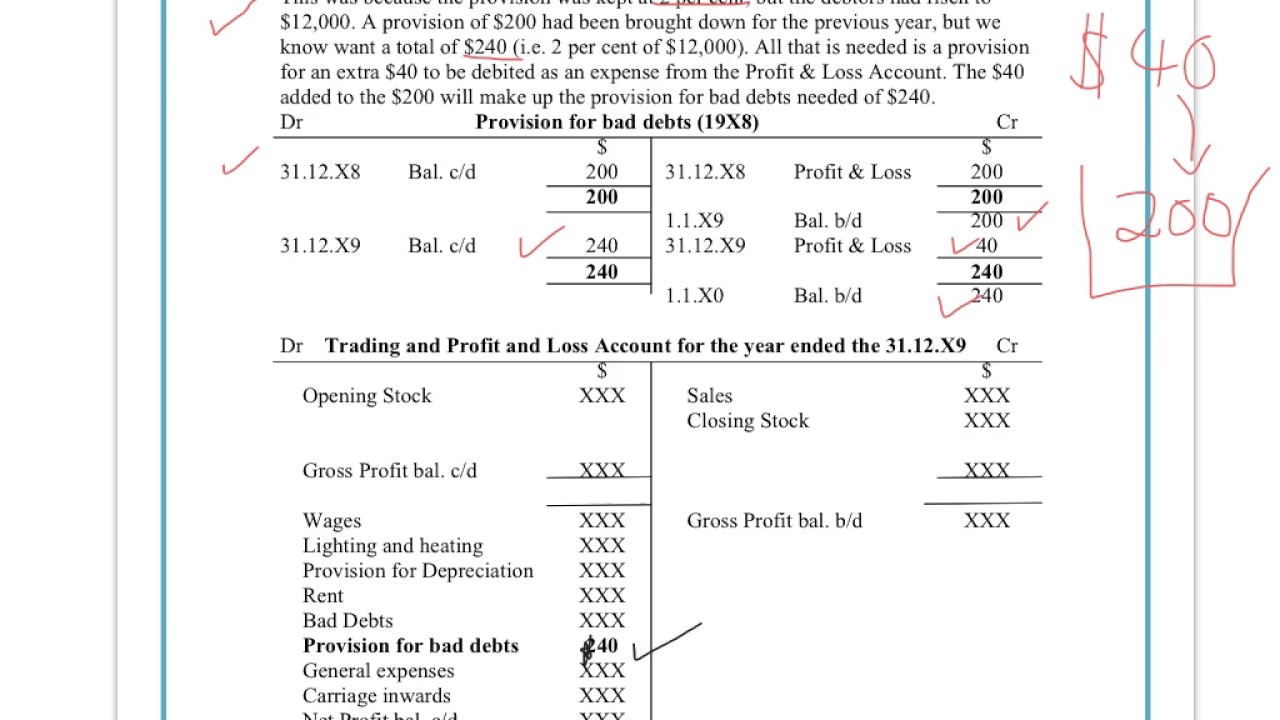
Fun Info About Reserve For Bad Debts In Balance Sheet Fees Earned On

An allowance for bad debt is a valuation account used to estimate the amount of a firm's receivables that may ultimately be uncollectible.
Reserve for bad debts in balance sheet. Wahab 131 1 1 2 add a comment 3 answers sorted by: Analysts keep track of changes in bad debt reserves, which can uncover other financial health problems in a company. But the bad debt provision.
A bad debt reserve is an amount set aside by a company or financial institution to account for receivables that may not be collected. Bad debt reserve in balance sheet. Reserves on the balance sheet guide | accountant town a reserve is a portion of proprietorship which has been set aside for some specific purpose.
Meanwhile, any bad debts that are directly written off reduce the accounts. Reserves and projections: The net receivable balance is.
Balance sheet reserves, also known as claims reserves, are accounting entries that show money set aside to pay future obligations. Provision for doubtful debts is shown in the debit. It helps a company plan its cash flow needs.
It has been 1 year & the customer has not paid yet. Can you show treatment of provision for doubtful debts in balance sheet? The bad debt reserve is the amount of.
Similarly, a bad debt reserve is made by an entity in case the customers default. You track bad debts on the balance sheet as well, using the bad debt reserve account, also known as an allowance for bad debt. 4 the accounting equation is like so:
The allowance for doubtful accounts resides on the balance sheet as a contra asset. Bad debt is basically an expense for the company, recorded under the heading of sales and general administrative expenses. Suppose you sold 1000 bottles at $ 5 each on credit to a customer & that makes $ 5000 receivable.
Once doubtful debt for a certain period is realized and becomes bad debt, the actual amount of bad debt is written off the balance sheet—often referred to as. This includes how effectively a company manages the credit it extends to customers. Most companies and banks keep a bad debt reserve because some percentage of customers will fail to pay.
Bad debt reserve, also called an allowance for doubtful accounts (ada), is a reduction in a company's accounts receivable. Maintaining a bad debt reserve and projecting bad debt based on past data and current trends are essential for anticipating and managing the risk of bad. A bad debt reserve, also known as the allowance for doubtful accounts, is the amount of provision made by the company against the accounts receivable present in the books of.
For example, a balance sheet may reveal $1,000,000 of accounts receivable, against which is offset $50,000 of bad debt reserve. An allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra account that nets against the total receivables presented on the balance sheet to reflect only the amounts expected to be paid. Explanation reserve means the accumulation of something for a purpose.


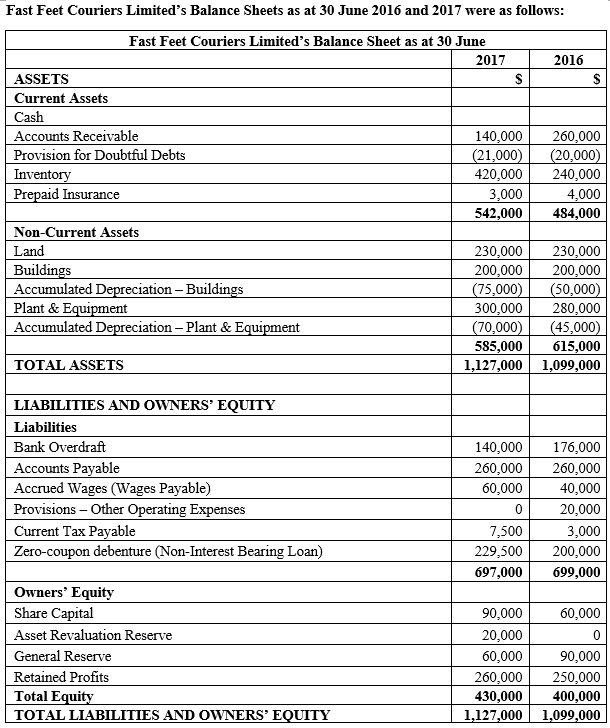






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/baddebtreserve.asp_final-2e6562d79b874ef39946ab765138946a.png)